关于MapReduce
2025/4/18大约 8 分钟
go-zero 的并发利器 mr 在业务中的应用
1. 查询异常
原查询如下: 这是一个告警 List 接口,其中 filters.SnowflakeIdList 会根据传入的 雪花ID 来过滤其对应范围内的告警数据,但当其长度十分大时,对应的 SQL 会超过 65535 个长度,从而触发异常 Error 1390 (HYooo): Prepared statement contains too many placeholders.
func (slr *SyncLogRecordRepo) List(ctx context.Context, filters *vo.LogRecordListFilter, fields []string) ([]*entities.SyncLogRecord, error) {
var dbInfos []models.SyncLogRecord
// 增加查询超时
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(ctx, 60*time.Second)
defer cancel()
query := slr.DbPool.Scopes(models.ActiveRecord).WithContext(ctx).Model(&models.SyncLogRecord{})
if filters.PageSize <= 0 {
filters.PageSize = 20
}
offset := int32(0)
if filters.Current > 1 {
offset = filters.PageSize * (filters.Current - 1)
}
if fields != nil && len(fields) > 0 {
query.Select(fields)
}
query = formatQuery(query, &LogRecordQueryBase{
Keyword: filters.Keyword,
StartDate: filters.StartDate,
EndDate: filters.EndDate,
AlgorithmIdList: filters.AlgorithmIdList,
Archived: filters.Archived,
HandleStatus: filters.HandleStatus,
LogType: filters.LogType,
WhetherAlert: filters.WhetherAlert,
CameraUuidList: filters.CameraUuidList,
SnowflakeIdList: filters.SnowflakeIdList,
IDList: filters.IDList,
SystemID: filters.SystemID,
})
result := query.Order(fmt.Sprintf("%s %s", filters.GetSortField(), filters.GetSortType())).Limit(int(filters.PageSize)).Offset(int(offset)).Find(&dbInfos)
if result.Error != nil {
return nil, result.Error
}
var entityList []*entities.SyncLogRecord
for _, dbInfo := range dbInfos {
entityList = append(entityList, dbInfo.TransToEntity())
}
return entityList, nil
}此时,理所当然会考虑进行批处理分批查询并处理然后聚合,即 MapReduce
2. MapReduce
2.1 概念及基本使用
MapReduce: 一种编程模型,使用并行处理来加速大规模数据处理过程。可在 Hadoop 集群中的数百或数千台服务器之间实现大规模可扩展性。
function map(String name, String document):
// name: document name
// document: document contents
for each word w in document:
emit (w, 1)
function reduce(String word, Iterator partialCounts):
// word: a word
// partialCounts: a list of aggregated partial counts
sum = 0
for each pc in partialCounts:
sum += pc
emit (word, sum)其核心思想是“分而治之”
- Mapper负责“分”: ,即把复杂的任务分解为若干个“简单的任务”来处理。“简单的任务” 包含三层含义:
- 数据或计算的规模相对原任务要大大 缩小 ;
- 就近计算原则,即任务会分配到存放着所需数据的节点上进行计算;
- 小任务可以并行计算,彼此间几乎没有依赖关系;
- Reducer: 负责对 map 阶段的结果进行汇总。
2.2 go-zero的mr源码
package mr
import (
"context"
"errors"
"source/errorx"
"sync"
"sync/atomic"
)
const (
defaultWorkers = 16
minWorkers = 1
)
var (
// ErrCancelWithNil is an error that mapreduce was cancelled with nil.
ErrCancelWithNil = errors.New("mapreduce cancelled with nil")
// ErrReduceNoOutput is an error that reduce did not output a value.
ErrReduceNoOutput = errors.New("reduce not writing value")
)
type (
// ForEachFunc is used to do element processing, but no output.
ForEachFunc[T any] func(item T)
// GenerateFunc is used to let callers send elements into source.
GenerateFunc[T any] func(source chan<- T)
// MapFunc is used to do element processing and write the output to writer.
MapFunc[T, U any] func(item T, writer Writer[U])
// MapperFunc is used to do element processing and write the output to writer,
// use cancel func to cancel the processing.
MapperFunc[T, U any] func(item T, writer Writer[U], cancel func(error))
// ReducerFunc is used to reduce all the mapping output and write to writer,
// use cancel func to cancel the processing.
ReducerFunc[U, V any] func(pipe <-chan U, writer Writer[V], cancel func(error))
// VoidReducerFunc is used to reduce all the mapping output, but no output.
// Use cancel func to cancel the processing.
VoidReducerFunc[U any] func(pipe <-chan U, cancel func(error))
// Option defines the method to customize the mapreduce.
Option func(opts *mapReduceOptions)
mapperContext[T, U any] struct {
ctx context.Context
mapper MapFunc[T, U]
source <-chan T
panicChan *onceChan
collector chan<- U
doneChan <-chan struct{}
workers int
}
mapReduceOptions struct {
ctx context.Context
workers int
}
// Writer interface wraps Write method.
Writer[T any] interface {
Write(v T)
}
)
// Finish runs fns parallelly, cancelled on any error.
func Finish(fns ...func() error) error {
if len(fns) == 0 {
return nil
}
return MapReduceVoid(func(source chan<- func() error) {
for _, fn := range fns {
source <- fn
}
}, func(fn func() error, writer Writer[any], cancel func(error)) {
if err := fn(); err != nil {
cancel(err)
}
}, func(pipe <-chan any, cancel func(error)) {
}, WithWorkers(len(fns)))
}
// FinishVoid runs fns parallelly.
func FinishVoid(fns ...func()) {
if len(fns) == 0 {
return
}
ForEach(func(source chan<- func()) {
for _, fn := range fns {
source <- fn
}
}, func(fn func()) {
fn()
}, WithWorkers(len(fns)))
}
// ForEach maps all elements from given generate but no output.
func ForEach[T any](generate GenerateFunc[T], mapper ForEachFunc[T], opts ...Option) {
options := buildOptions(opts...)
panicChan := &onceChan{channel: make(chan any)}
source := buildSource(generate, panicChan)
collector := make(chan any)
done := make(chan struct{})
go executeMappers(mapperContext[T, any]{
ctx: options.ctx,
mapper: func(item T, _ Writer[any]) {
mapper(item)
},
source: source,
panicChan: panicChan,
collector: collector,
doneChan: done,
workers: options.workers,
})
for {
select {
case v := <-panicChan.channel:
panic(v)
case _, ok := <-collector:
if !ok {
return
}
}
}
}
// MapReduce maps all elements generated from given generate func,
// and reduces the output elements with given reducer.
func MapReduce[T, U, V any](generate GenerateFunc[T], mapper MapperFunc[T, U], reducer ReducerFunc[U, V],
opts ...Option) (V, error) {
panicChan := &onceChan{channel: make(chan any)}
source := buildSource(generate, panicChan)
return mapReduceWithPanicChan(source, panicChan, mapper, reducer, opts...)
}
// MapReduceChan maps all elements from source, and reduce the output elements with given reducer.
func MapReduceChan[T, U, V any](source <-chan T, mapper MapperFunc[T, U], reducer ReducerFunc[U, V],
opts ...Option) (V, error) {
panicChan := &onceChan{channel: make(chan any)}
return mapReduceWithPanicChan(source, panicChan, mapper, reducer, opts...)
}
// mapReduceWithPanicChan maps all elements from source, and reduce the output elements with given reducer.
func mapReduceWithPanicChan[T, U, V any](source <-chan T, panicChan *onceChan, mapper MapperFunc[T, U],
reducer ReducerFunc[U, V], opts ...Option) (val V, err error) {
options := buildOptions(opts...)
// output is used to write the final result
output := make(chan V)
defer func() {
// reducer can only write once, if more, panic
for range output {
panic("more than one element written in reducer")
}
}()
// collector is used to collect data from mapper, and consume in reducer
collector := make(chan U, options.workers)
// if done is closed, all mappers and reducer should stop processing
done := make(chan struct{})
writer := newGuardedWriter(options.ctx, output, done)
var closeOnce sync.Once
// use atomic type to avoid data race
var retErr errorx.AtomicError
finish := func() {
closeOnce.Do(func() {
close(done)
close(output)
})
}
cancel := once(func(err error) {
if err != nil {
retErr.Set(err)
} else {
retErr.Set(ErrCancelWithNil)
}
drain(source)
finish()
})
go func() {
defer func() {
drain(collector)
if r := recover(); r != nil {
panicChan.write(r)
}
finish()
}()
reducer(collector, writer, cancel)
}()
go executeMappers(mapperContext[T, U]{
ctx: options.ctx,
mapper: func(item T, w Writer[U]) {
mapper(item, w, cancel)
},
source: source,
panicChan: panicChan,
collector: collector,
doneChan: done,
workers: options.workers,
})
select {
case <-options.ctx.Done():
cancel(context.DeadlineExceeded)
err = context.DeadlineExceeded
case v := <-panicChan.channel:
// drain output here, otherwise for loop panic in defer
drain(output)
panic(v)
case v, ok := <-output:
if e := retErr.Load(); e != nil {
err = e
} else if ok {
val = v
} else {
err = ErrReduceNoOutput
}
}
return
}
// MapReduceVoid maps all elements generated from given generate,
// and reduce the output elements with given reducer.
func MapReduceVoid[T, U any](generate GenerateFunc[T], mapper MapperFunc[T, U],
reducer VoidReducerFunc[U], opts ...Option) error {
_, err := MapReduce(generate, mapper, func(input <-chan U, writer Writer[any], cancel func(error)) {
reducer(input, cancel)
}, opts...)
if errors.Is(err, ErrReduceNoOutput) {
return nil
}
return err
}
// WithContext customizes a mapreduce processing accepts a given ctx.
func WithContext(ctx context.Context) Option {
return func(opts *mapReduceOptions) {
opts.ctx = ctx
}
}
// WithWorkers customizes a mapreduce processing with given workers.
func WithWorkers(workers int) Option {
return func(opts *mapReduceOptions) {
if workers < minWorkers {
opts.workers = minWorkers
} else {
opts.workers = workers
}
}
}
func buildOptions(opts ...Option) *mapReduceOptions {
options := newOptions()
for _, opt := range opts {
opt(options)
}
return options
}
func buildSource[T any](generate GenerateFunc[T], panicChan *onceChan) chan T {
source := make(chan T)
go func() {
defer func() {
if r := recover(); r != nil {
panicChan.write(r)
}
close(source)
}()
generate(source)
}()
return source
}
// drain drains the channel.
func drain[T any](channel <-chan T) {
// drain the channel
for range channel {
}
}
func executeMappers[T, U any](mCtx mapperContext[T, U]) {
var wg sync.WaitGroup
defer func() {
wg.Wait()
close(mCtx.collector)
drain(mCtx.source)
}()
var failed int32
pool := make(chan struct{}, mCtx.workers)
writer := newGuardedWriter(mCtx.ctx, mCtx.collector, mCtx.doneChan)
for atomic.LoadInt32(&failed) == 0 {
select {
case <-mCtx.ctx.Done():
return
case <-mCtx.doneChan:
return
case pool <- struct{}{}:
item, ok := <-mCtx.source
if !ok {
<-pool
return
}
wg.Add(1)
go func() {
defer func() {
if r := recover(); r != nil {
atomic.AddInt32(&failed, 1)
mCtx.panicChan.write(r)
}
wg.Done()
<-pool
}()
mCtx.mapper(item, writer)
}()
}
}
}
func newOptions() *mapReduceOptions {
return &mapReduceOptions{
ctx: context.Background(),
workers: defaultWorkers,
}
}
func once(fn func(error)) func(error) {
once := new(sync.Once)
return func(err error) {
once.Do(func() {
fn(err)
})
}
}
type guardedWriter[T any] struct {
ctx context.Context
channel chan<- T
done <-chan struct{}
}
func newGuardedWriter[T any](ctx context.Context, channel chan<- T, done <-chan struct{}) guardedWriter[T] {
return guardedWriter[T]{
ctx: ctx,
channel: channel,
done: done,
}
}
func (gw guardedWriter[T]) Write(v T) {
select {
case <-gw.ctx.Done():
return
case <-gw.done:
return
default:
gw.channel <- v
}
}
type onceChan struct {
channel chan any
wrote int32
}
func (oc *onceChan) write(val any) {
if atomic.CompareAndSwapInt32(&oc.wrote, 0, 1) {
oc.channel <- val
}
}3. 优化批处理
该查询场景十分契合其分治并行处理的形式,且分批提高性能(无需 sleep ),故优化后如下:
func (slr *SyncLogRecordRepo) List(ctx context.Context, filters *vo.LogRecordListFilter, fields []string) ([]*entities.SyncLogRecord, error) {
var dbInfos []models.SyncLogRecord
// 增加查询超时
sqlCtx, sqlCancel := context.WithTimeout(ctx, 60*time.Second)
defer sqlCancel()
if len(filters.SnowflakeIdList) < listRecordBatchSize {
query := slr.DbPool.Scopes(models.ActiveRecord).WithContext(sqlCtx).Model(&models.SyncLogRecord{})
if filters.PageSize <= 0 {
filters.PageSize = 20
}
offset := int32(0)
if filters.Current > 1 {
offset = filters.PageSize * (filters.Current - 1)
}
if fields != nil && len(fields) > 0 {
query.Select(fields)
}
query = formatQuery(query, &LogRecordQueryBase{
Keyword: filters.Keyword,
StartDate: filters.StartDate,
EndDate: filters.EndDate,
AlgorithmIdList: filters.AlgorithmIdList,
Archived: filters.Archived,
HandleStatus: filters.HandleStatus,
LogType: filters.LogType,
WhetherAlert: filters.WhetherAlert,
CameraUuidList: filters.CameraUuidList,
SnowflakeIdList: filters.SnowflakeIdList,
IDList: filters.IDList,
SystemID: filters.SystemID,
})
result := query.Order(fmt.Sprintf("%s %s", filters.GetSortField(), filters.GetSortType())).Limit(int(filters.PageSize)).Offset(int(offset)).Find(&dbInfos)
if result.Error != nil {
return nil, result.Error
}
var entityList []*entities.SyncLogRecord
for _, dbInfo := range dbInfos {
entityList = append(entityList, dbInfo.TransToEntity())
}
return entityList, nil
}
// map reduce
batches := splitIds(filters.SnowflakeIdList, listRecordBatchSize)
logx.Debugf("List Log, batch: %d, batch Size:%d", len(batches), listRecordBatchSize)
generateFunc := func(source chan<- []int64) {
for _, batch := range batches {
source <- batch
}
}
mapperFunc := func(batch []int64, writer mr.Writer[[]*entities.SyncLogRecord], cancel func(error)) {
query := slr.DbPool.Scopes(models.ActiveRecord).WithContext(ctx).Model(&models.SyncLogRecord{})
if filters.PageSize <= 0 {
filters.PageSize = 20
}
offset := int32(0)
if filters.Current > 1 {
offset = filters.PageSize * (filters.Current - 1)
}
if fields != nil && len(fields) > 0 {
query.Select(fields)
}
query = formatQuery(query, &LogRecordQueryBase{
Keyword: filters.Keyword,
StartDate: filters.StartDate,
EndDate: filters.EndDate,
AlgorithmIdList: filters.AlgorithmIdList,
Archived: filters.Archived,
HandleStatus: filters.HandleStatus,
LogType: filters.LogType,
WhetherAlert: filters.WhetherAlert,
CameraUuidList: filters.CameraUuidList,
SnowflakeIdList: batch,
IDList: filters.IDList,
SystemID: filters.SystemID,
})
result := query.Order(fmt.Sprintf("%s %s", filters.GetSortField(), filters.GetSortType())).
Limit(int(filters.PageSize)).Offset(int(offset)).Find(&dbInfos)
if result.Error != nil {
cancel(result.Error)
return
}
var entityList []*entities.SyncLogRecord
for _, dbInfo := range dbInfos {
entityList = append(entityList, dbInfo.TransToEntity())
}
writer.Write(entityList)
}
reducerFunc := func(pipe <-chan []*entities.SyncLogRecord, writer mr.Writer[[]*entities.SyncLogRecord], cancel func(error)) {
var all []*entities.SyncLogRecord
for batch := range pipe {
all = append(all, batch...)
}
writer.Write(all)
}
result, err := mr.MapReduce(generateFunc, mapperFunc, reducerFunc, mr.WithContext(sqlCtx), mr.WithWorkers(8))
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return result, nil
}修改后的 SQL 打印如下:
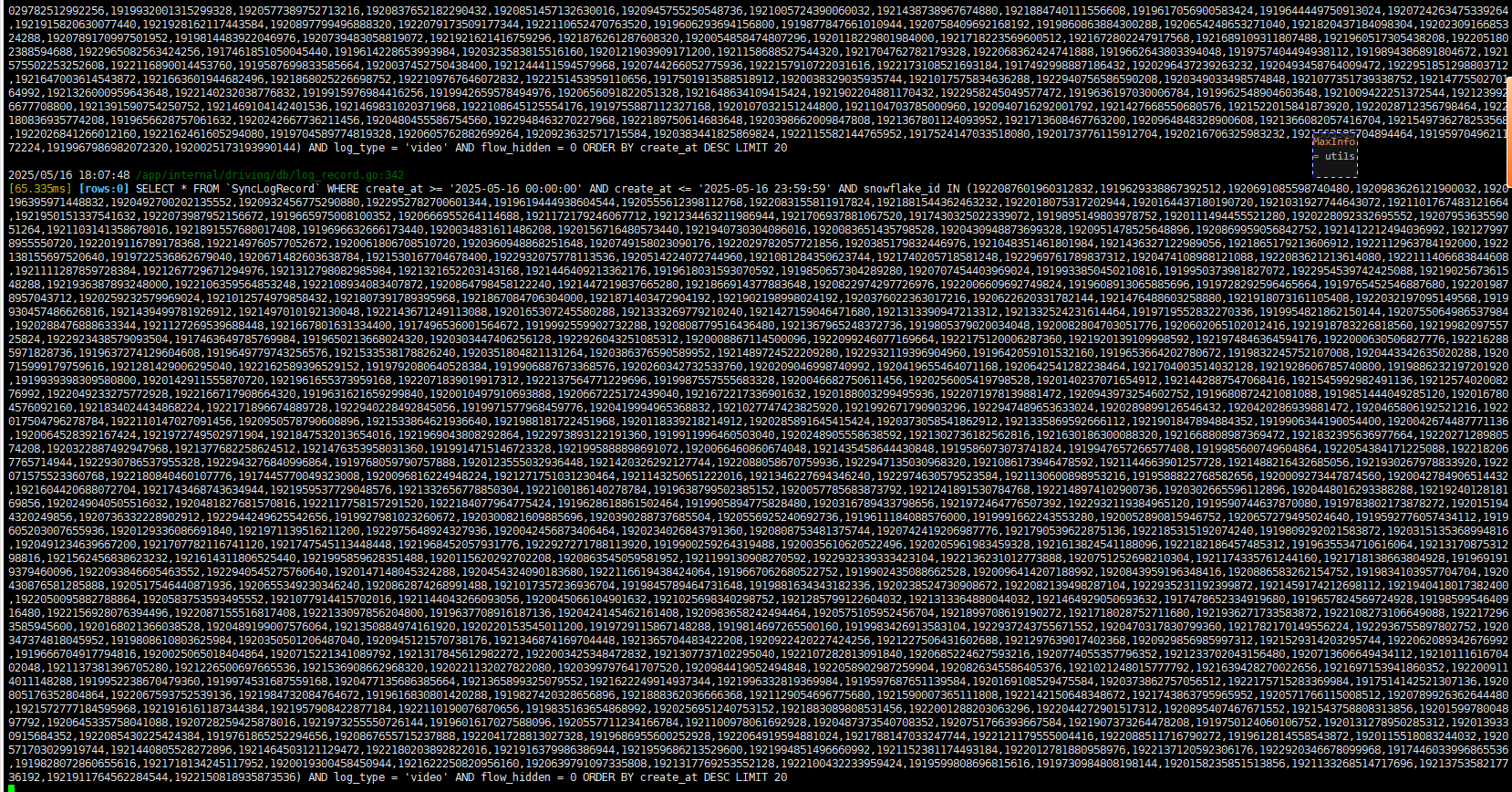
测试并调整并发:
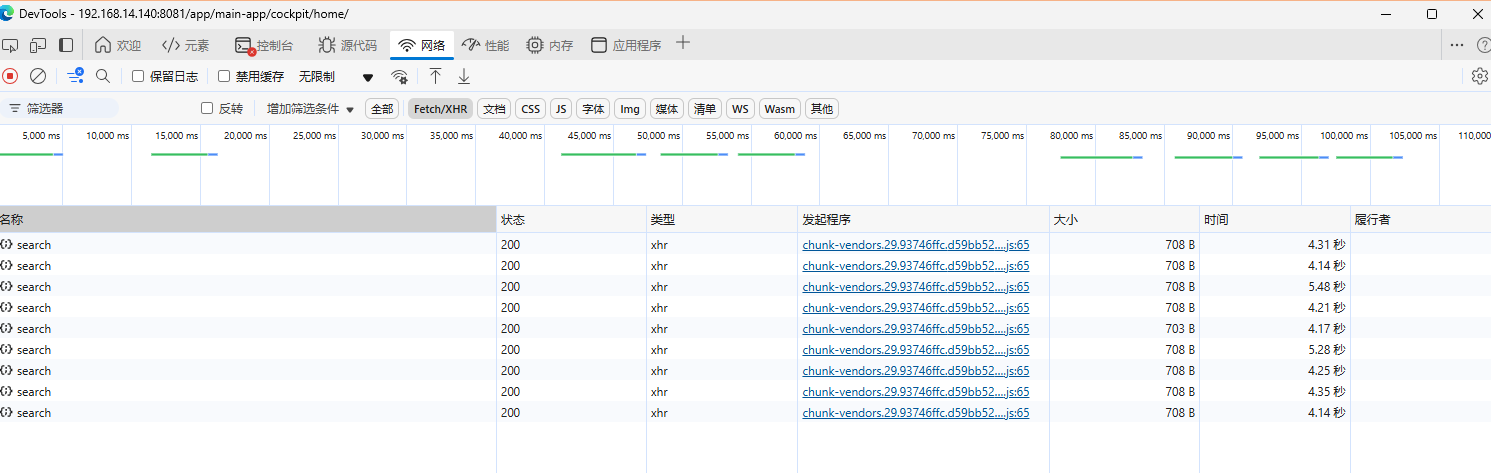
160 batch * 1000 size = 16W 数据量, 4 worker

32 batch * 5000 size = 16W 数据量, 8 worker
FindInBatches
FindInBatches 允许分批查询和处理记录。 这对于有效地处理大型数据集、减少内存使用和提高性能尤其有用。
使用FindInBatches, GORM 处理指定批大小的记录。 在批处理功能中,您可以对每批记录应用操作。
// 处理记录,批处理大小为100
result := db.Where("processed = ?", false).FindInBatches(&results, 100, func(tx *gorm.DB, batch int) error {
for _, result := range results {
// 对批中的每条记录进行操作
}
// 保存对当前批记录的修改
tx.Save(&results)
// tx.RowsAffected 提供当前批处理中记录的计数(the count of records in the current batch)
// 'batch' 变量表示当前批号(the current batch number)
// 返回 error 将阻止更多的批处理
return nil
})
// result.Error 包含批处理过程中遇到的任何错误
// result.RowsAffected 提供跨批处理的所有记录的计数(the count of all processed records across batches)